Project Description
Background on Copper Recovery
Copper mining typically encompasses separating sulfide ore and recovery of purer metal particles from gangue minerals using froth flotation. The sulfide ore is then crushed, grinded and milled into fine particles. These fine particles then mix with water into a slurry, feeding into a flotation cell.
An agitator at the bottom of the cell stirs the slurry (also called pulp) and suspends the particles in the mix. Air supplied to the cell through the agitator creates bubbles, which rise to the top of the tank, creating the froth. The addition of chemicals to the tank enables the metal particles to attach themselves to the bubbles as they rise to the surface. The “tailings,” or residue, remaining in the slurry exit an outlet in the base of the tank and are generally discharged to a tailing pond.
Why REXA?
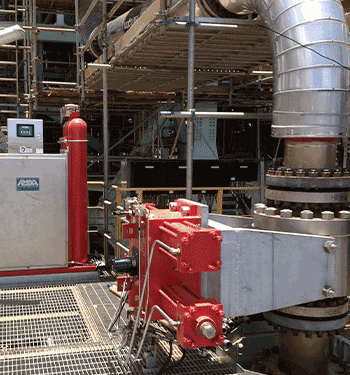
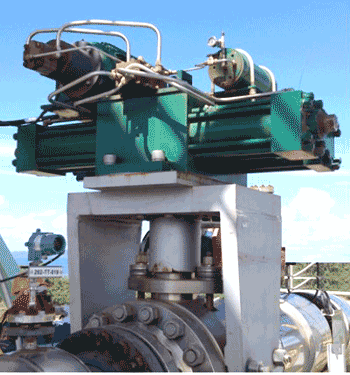
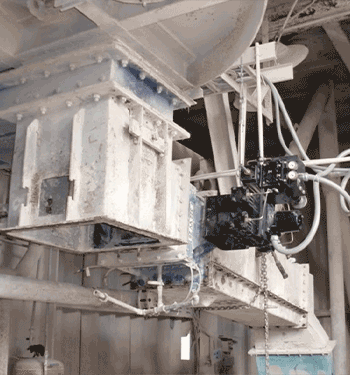
Most mines rely on pneumatic actuators to control the pulp height in flotation cells via modulating dart valves. Unfortunately, even with the use of smart positioners, these actuators cannot control or maintain the proper pulp level due to the compressibility of air.
Thanks to REXA’s unique Electraulic™ technology, our actuators improve flotation level control by precisely modulating the opening and closing of each tank’s dart valves.
Read more about improving copper recovery within flotation cells in our full Application Spotlight below. You can also watch our Application Video for more of a visual experience!